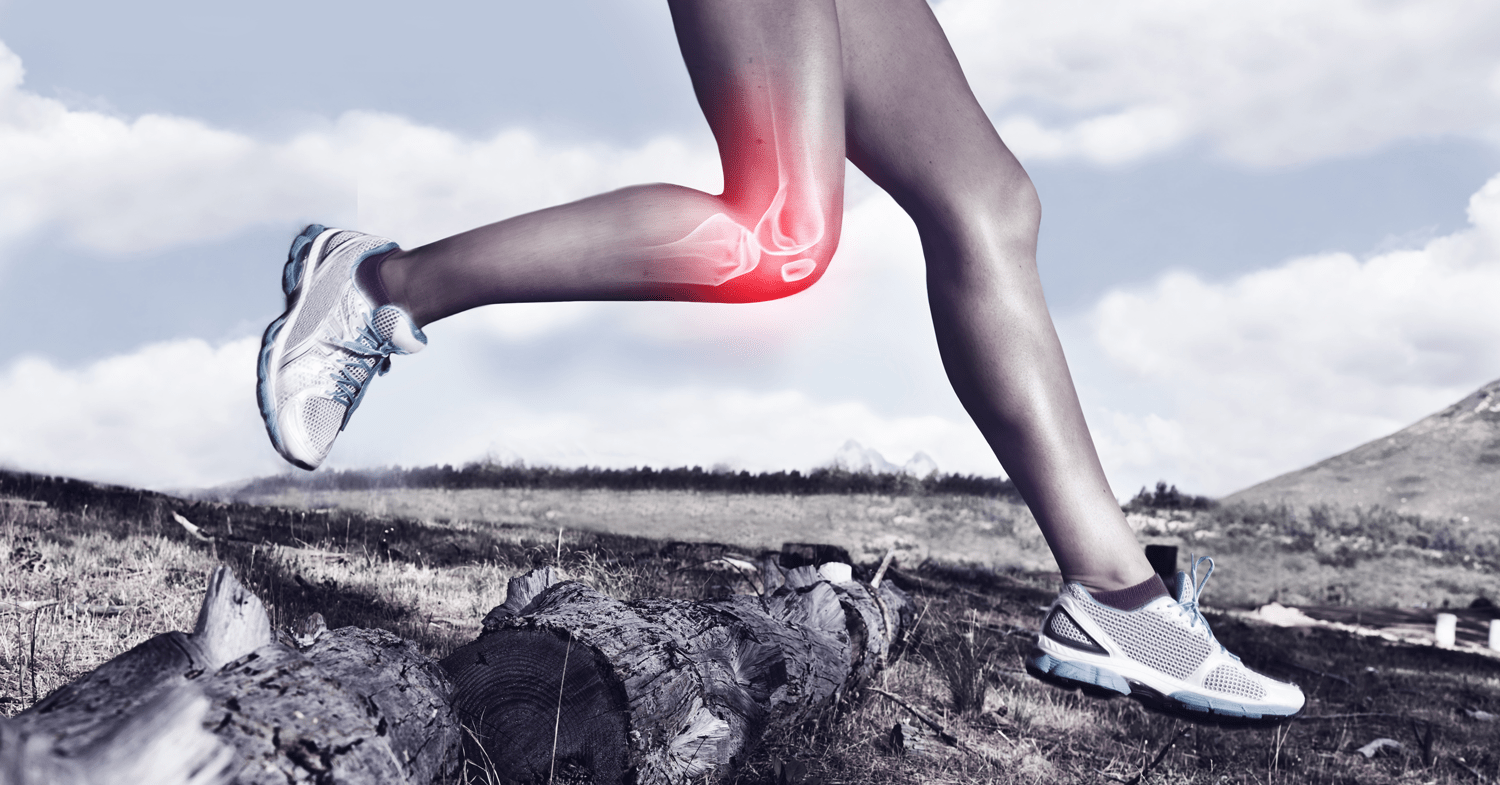
Acute inflammation:
One of the most underrated facts about inflammation is that it’s an integral function of the body. One of the most important aspects of the inflammatory process is that it is part of the healing process in the body and it stimulates the immune system to defend the body from harmful agents like bacteria and viruses.
While it might not seem like a beneficial process at the time, inflammation from physical juries that follow with redness, swelling, warmth, pain and sometimes loss of function or motion, act as a protective mechanism for the body. Let's call this the “good” inflammation, as it promotes healing and recovery.
Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation:
Inflammation gets a bad wrap it becomes chronic. In this case, an underlying issue in the body is constantly signalling the body to release inflammatory cytokines. Chronic inflammation can be detrimental to the body and is associated with various diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and bowel diseases.

Autoimmune related inflammation
diseases are just one of many chronic diseases that are associated with signs and symptoms of inflammation. The signs and symptoms of an autoimmune disease appear when the body mistakenly perceives its own cells or tissues as harmful and starts attacking its own cells. This is when inflammation goes into overdrive and causes damage to joints and internal organs. While autoimmune diseases can be hereditary, we can manage the severity of the inflammation reaction through diet, exercise, and lifestyle coupled with or without medication.
What you choose to eat
In today’s society, consumption of highly processed food products dominates our diet. Many of which lack essential nutrients and fiber. This is thought to contribute to our susceptibility to chronic inflammatory health conditions.
Our gut microflora is an important link between what we eat and our immune system. Our intestinal system is home to a community of trillions of bacteria.. Evidence suggests that bacteria can adapt to the foods we eat. However, the changes made by the bacteria can have a positive and a negative affect on our health. Depending on the nutrients that we take in, some bacteria may process these nutrients in an undesirable way, resulting in the production of by products that have the potential to trigger an autoimmune response in the gut.
If these toxic by products are absorbed into the body in significant quantities, similar immune responses may be triggered in other tissues and organs throughout the body. If this insult continues for a significant amount of time, the body may start to see itself as foreign and an autoimmune disorder may develop along with signs and symptoms of a chronic inflammatory condition. But not all bacteria respond in the same way.
Other gut bacteria may attempt to neutralize the toxic by-products and inhibit the inflammatory response in the gut and other reactions in other tissues. For example, the expansion of the bacterial species referred to as Bacteroides fragilis, has been shown to A healthy gut equals a healthy body and a healthy mind. The gut microflora is that powerful.
Fun fact: Aside from the cognitive benefits, omega-3 supplementation can modulate the gut microbiota so much that they can be considered a prebiotic. Another added benefit of Omega-3 is its role as an inflammatory response suppressor by interfering with the synthesis of the pro-inflammatory eicosanoids. To help manage inflammation, Omega Supper 800 from Platinum Naturals is an excellent product.
So, what do you eat?
One of the most researched anti-inflammatory ways of eating is the Mediterranean diet; it favours plant-based foods that are rich in fruits and vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fish. There are numerous variations to this diet including the popular Paleo diet. What these diets have in common is the consumption of whole foods. Whole foods contain important antioxidants and phytochemicals that are powerful anti-inflammatory nutrients.
Exercise is Medicine
Regular physical activity is associated with overall health promotion and disease prevention, including weight management. Research has shown that one session of moderate 20-minute exercise has anti-inflammatory effects (Dimitroy, Hulteng, & Hong, 2017).
The mechanism of action starts during exercise, where the muscle cells release a small protein known as IL-6, which stands for interleukin 6. IL-6 initiates anti-inflammatory actions in 2 ways, first by lowering TNF alpha levels and second by inhibiting the signalling pathway of interleukin 1 beta, both of which are proteins that trigger inflammation.
IL-6 is not the only factor involved in the anti-inflammatory process. Another mechanism of action includes hormones such as epinephrine and norepinephrine that trigger adrenergic receptors that release cytokines that regulate systemic inflammation and induce immune responses
Lifestyle factors
Lifestyle factors that can increase inflammation in the body include smoking, obesity, stress, and sleep problem and may increase the risk of chronic inflammation.
Over the years stress has increased dramatically. Stress can be either in the form of physical, mental, or emotional. Stress may be the precursor of many human diseases, as it is associated with the body losing its ability to regulate the inflammatory response. To elaborate, stress induces the “fight-or-flight response” in the body, which then activates the release of the stress hormone cortisol. This increases inflammatory markers in the body and promotes the growth of undesirable gut microbes.
There are many ways to manage stress; this includes deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga. One study found that individuals who practice meditation regularly showed lower levels of cortisol and inflammatory markers.
It’s important to find just a few minutes a day to relax, unwind, and enjoy the moment. Other ways to manage stress are by supporting the body with the use of stress supplements, such as Easymulti Stress from Platinum Naturals. Another great option is EasyMag by Platinum Naturals, which features Magnesium Bisglycinate, Magnesium has been shown in research to improve sleep quality and reduce stress.
Supplementation
Did you know some supplements may help to reduce inflammation in the body? Here are a few products that may help to get you started:
InflaCare-X combines proteolytic enzymes with anti-inflammatories: Boswellia, cat’s claw, cayenne fruit, deglycyrrhizinated licorice, devils claw root, and turmeric root. These botanicals are known to help to reduce symptoms of inflammation, swelling, and pain.
Relev-X has similar anti-inflammatory ingredients as InflaCare-X, with the addition of glucosamine HCL for healthy cartilage and fish oil for joint and overall health. This is intended for those who want to prevent further damage and rebuild their cartilage as well as reduce pain and symptoms of inflammation.